SIDP advocates a One Health approach to antimicrobial stewardship initiatives. A One Health approach recognizes the interconnection between people, animals, plants, and the environment. This approach encompasses many issues such as anticipating, preventing, detecting, and controlling diseases that spread between humans and animals, preventing and addressing antimicrobial resistance, and improving food and water safety.
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines One Health as “an integrated, unifying approach that aims to sustainably balance and optimize the health of humans, animals, and ecosystems.” | 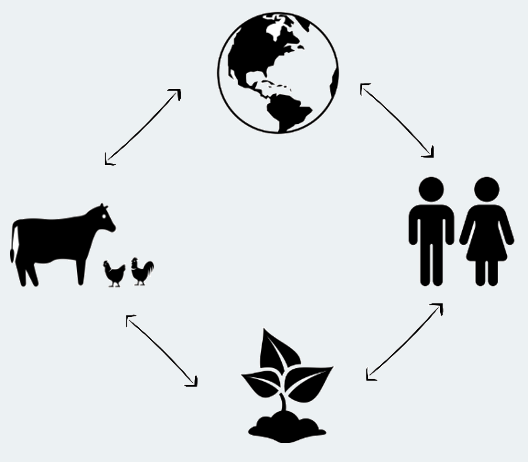 |
Why is One Health important?
|
60% of pathogens (or germs) that cause disease in humans originate from animals |
both domestic and wild animals can lead to more diseases passed between animals and people
|
|
250,000 additional deaths per year expected from climate change between 2030 and 2050 |
environments and lead to more disease in animals
|
products via international travel and trade can lead
to a rapid spread of diseases around the world
|
What are common One Health issues?
Common One Health issues include:
- Zoonotic diseases - Diseases that spread between animals and people
-
- April 2025: An emerging zoonotic disease is the H5 bird flu, which is spreading from wild birds to poultry, cows, and cats, and from these animals to humans. Refer to the CDC to keep up to date on this situation.
- Vector-borne diseases - Diseases that are transmitted to humans and other animals by blood-feeding arthropods, such as mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas
- Antimicrobial resistance - Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens can quickly spread between the environment, animals, and people making it harder to treat certain infections
- Food safety and security - Diseases, pests, chemical treatments in plants and animals used for food can threaten people, livelihoods, and economies
- Environmental contamination - Contamination of water and/or lack of access to clean water can make people and animals sick
- Climate change - Disruptions in the environment, such as deforestation, can result in diseases passing to animals and humans
The Foundation of One Health
One Health requires a multidisciplinary approach among professionals in:
- Human health (e.g., physicians, nurses, pharmacists, public health practitioners, epidemiologists)
- Animal health (e.g., veterinarians, agricultural workers)
- Environmental health (e.g., ecologists, wildlife experts)
- Others
Goals of a One Health Approach
According to the CDC, the One Health approach can:
- Prevent outbreaks of zoonotic disease in animals and people
- Improve food and water safety and security
- Reduce antimicrobial-resistant infections and improve human and animal health
- Protect global health security
- Protect environmental biodiversity and conservation
SIDP One Health Education Handouts
|
|
One Health Overview for Providers |
|
|
|
|
Resources
Handout References
- One Health Overview for Patients
- CDC. (2024, October 30). About One Health
- One Health Overview for Providers
- CDC. (2024, October 30). About One Health
- CDC. (2024, April 9). Healthy Pets, Healthy People: Clinical Resources
- Food Safety Handout for Patients
- CDC. (2024, April 9). About Four Steps to Food Safety
- FDA. (2025, May 12). Recalls, Market Withdrawals, & Safety Alerts
- Common Zoonotic Infections for Clinicians
- CDC. (2024, October 7). Clinical Overview of Salmonellosis
- CDC. The Many Forms of Lyme Disease Rashes (Erythema Migrans)
- CDC. (2024, May 15). Signs and Symptoms of Untreated Lyme Disease
-